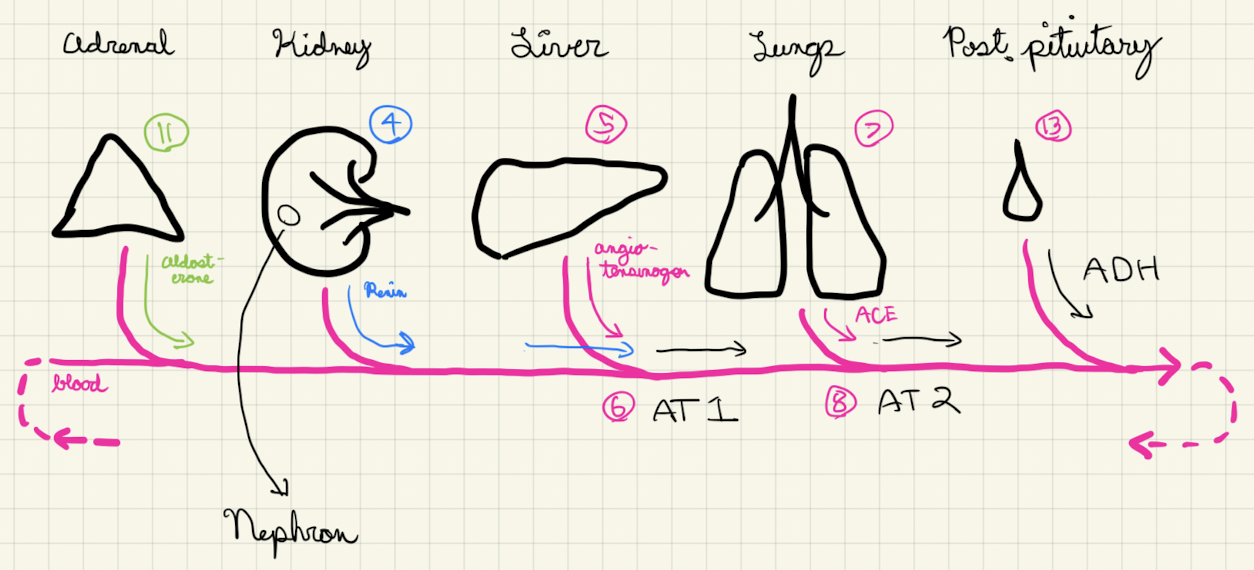
Renin Angotensinogen Aldosterone System (RAAS)
The RAAS maintains blood volume (and therefore blood pressure) by diluting or concentrating blood serum (and inversely, concentrating or diluting urine), among other mechanisms.
-
Renin is released from juxtaglomerular cells in the afferent arteriole of the nephron when...
-
The liver continuously stores and releases angiotensinogen into the blood stream.
- Renin converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I.
- AT1 is converted into angiotensin II by angiotensin converting enzyme produced in the lungs.
-
AT2 has multiple functions. AT2...
- triggers the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
- constricts the smooth muscle of the efferent arteriole, increasing glomerular filtration of blood, increasing amount of sodium in the DCT.
- promotes generalized vasoconstriction, increasing blood pressure and therefor GFR.
- triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone from the posterior pituitary gland, which decreases amount of H\(_2\)O in the DCT.
-
Aldosterone causes the DCT to reabsorb sodium into the ECF (and excrete potassium). Sodium draws water into the ECF via osmosis, increasing ECF volume.